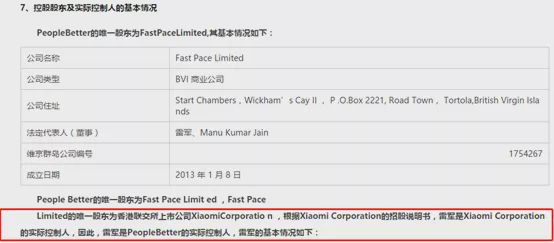
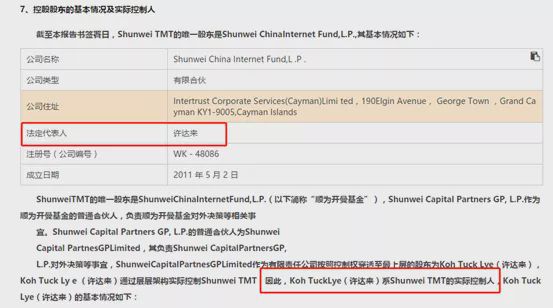
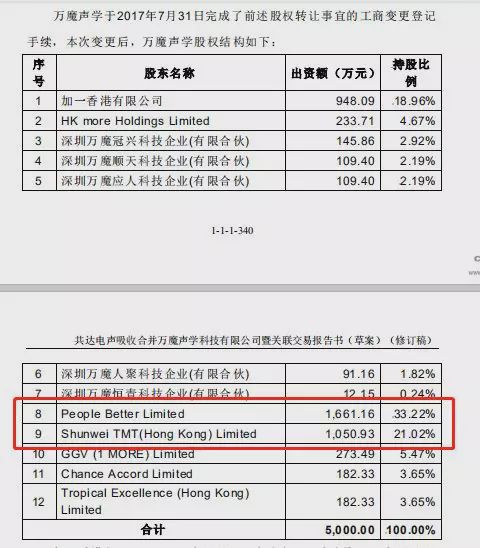
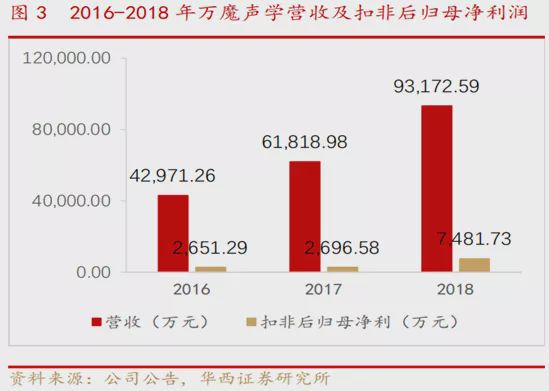
The Measures for the Supervision and Administration of Insurance Group Companies was adopted at the 10th Committee Meeting of China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission in 2021 on August 19th, 2021. It is hereby promulgated and shall come into force as of the date of promulgation.
Chairman Guo Shuqing
November 24, 2021
Measures for the supervision and administration of insurance group companies
Chapter I General Provisions
Article 1 In order to strengthen the supervision and management of insurance group companies, effectively prevent the operational risks of insurance groups, and promote the healthy development of financial and insurance industries, these Measures are formulated in accordance with the Insurance Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) (hereinafter referred to as the Insurance Law), the Company Law of People’s Republic of China (PRC) and other laws and administrative regulations, as well as the Decision of the State Council on Setting Administrative Permissions for Administrative Examination and Approval Items that Need to Be Retained (Order No.412 of the State Council of the People’s Republic of China).
Article 2 The Insurance Regulatory Commission of the Bank of China (hereinafter referred to as China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission) shall, in accordance with laws, administrative regulations and the State Council’s authorization, and on the principle that substance is more important than form, conduct comprehensive, continuous and penetrating supervision and management over insurance group companies.
Article 3 The term "insurance group company" as mentioned in these Measures refers to a company registered in accordance with the law and established with the approval of China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission, which has the words "insurance group" or "insurance holding" in its name and exercises control, joint control or significant influence on the member companies of the insurance group.
Insurance group refers to an enterprise collection composed of insurance group companies and companies controlled, jointly controlled or greatly influenced by them. In this enterprise collection, besides insurance group companies, there are more than two subsidiaries that are insurance companies and insurance business is the main business of this enterprise collection.
The member companies of an insurance group refer to insurance group companies and companies controlled, jointly controlled or greatly influenced by them, including insurance group companies, subsidiaries directly or indirectly controlled by insurance group companies and other member companies.
Chapter II Establishment and Licensing
Article 4 The establishment of an insurance group company shall be submitted to China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission for examination and approval and meet the following conditions:
(1) The investor meets the qualification requirements for shareholders of insurance companies as stipulated by China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission, and the shareholding structure is reasonable, and it controls at least 50% of the shares of two domestic insurance companies in total;
(2) Having member companies that meet the requirements of Article 6 of these Measures;
(3) The minimum registered capital is 2 billion yuan;
(4) Having directors, supervisors and senior managers who meet the qualification requirements stipulated by China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission;
(5) Having a sound corporate governance structure, sound organizational structure, effective risk management and internal control management system;
(6) Having business premises, office equipment and information systems suitable for its operation and management;
(seven) other conditions stipulated by laws, administrative regulations and China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission.
Involving the disposal of risks, the above conditions may be appropriately relaxed with the approval of China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission.
Article 5 The supervision of equity and shareholders’ behavior of insurance group companies shall be governed by China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission’s regulations on equity management of insurance companies.
Article 6 At least one insurance company controlled by the investor who intends to establish an insurance group company meets the following conditions:
(a) in China for more than 6 years;
(2) It has made continuous profits in the last three fiscal years;
(3) Its net assets at the end of the previous year are not less than 1 billion yuan, and its total assets are not less than 10 billion yuan;
(4) Having a sound corporate governance structure, sound organizational structure, effective risk management and internal control management system;
(5) The core solvency adequacy ratio is not less than 75% in the last four quarters, and the comprehensive solvency adequacy ratio is not less than 150%;
(6) Its comprehensive risk rating in the last four quarters is not lower than Class B;
(seven) in the last three years, there were no major violations of laws and regulations and major acts of dishonesty.
Article 7 An insurance group company may be established in the following two ways:
(1) Initiating the establishment. The shareholders of an insurance company, as promoters, set up an insurance group company with their equity and monetary contributions, of which the total monetary contribution shall not be less than 50% of the registered capital of the insurance group company.
(2) Renaming the establishment. An insurance company is renamed as an insurance group company, and the insurance group company establishes an insurance subsidiary with monetary contribution, and the insurance business of the original insurance company is transferred to the insurance subsidiary according to law.
The establishment of insurance group companies includes two stages: preparation and opening.
Article 8 Where an insurance group company is established by means of sponsorship, the sponsors shall submit the following materials to China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission in the preparatory stage:
An application for establishment, including the name, organizational form, registered capital, domicile (business premises), investors, investment amount, investment proportion, business scope, preparatory organization, contact person and contact information of the company to be established;
(2) Feasibility study report, including feasibility analysis, establishment mode, development strategy, corporate governance and organizational framework, risk management and internal control system, solvency evaluation of insurance subsidiaries before and after integration, etc.;
(3) the preparation plan, including the establishment of the preparatory group, work responsibilities and work plans, the equity structure of the insurance group company to be established and its subsidiaries, the overall planning and operation process for rationalizing the equity relationship, the name and business category of the subsidiaries, etc.;
(4) The materials of the person-in-charge of the preparatory group, including the investor’s letter of confirmation on the appointment of the person-in-charge of the preparatory group and the proposed chairman and general manager, the basic information of the person-in-charge of the preparatory group, the personal approval certificate, the application form for the qualification of the proposed chairman and general manager, the identity certificate and the copy of the academic degree certificate;
(5) Draft articles of association of the insurance group company;
(6) The audited financial report and solvency report of the insurance company controlled by the promoters in the last three years;
(7) Business license;
(8) Relevant materials of investors, including basic information materials, financial information materials, corporate governance materials, subsidiary information materials, special materials of investors in limited partnership enterprises, etc.;
(9) documents certifying the ownership or right to use the domicile (business premises);
(ten) long-term development strategy and planning, business plan, foreign investment plan, capital and financial management, risk management and internal control and other major systems;
(eleven) information construction report;
(twelve) legal opinions;
(13) Anti-money laundering materials;
(14) A statement on the authenticity of the materials;
(fifteen) other materials stipulated by China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission.
Article 9 Where an insurance group company is established by renaming, the insurance company to be renamed shall submit the following materials to China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission in the preparatory stage:
(1) An application for renaming, which shall specify the name, organizational form, registered capital, domicile (business premises), business scope, preparatory organization, contact person and contact information of the company to be renamed;
(2) Feasibility study report, including feasibility analysis, renaming method, corporate governance and organizational framework, development strategy, risk management and internal control system, and solvency assessment of insurance companies before and after renaming;
(3) The name change plan, including the equity structure of the insurance group company to be established and its subsidiaries, the overall planning and operation process for rationalizing the equity relationship, the name and business category of the subsidiaries, etc.;
(4) The materials of the person-in-charge of the preparatory group, including the investor’s letter of confirmation on the appointment of the person-in-charge of the preparatory group and the proposed chairman and general manager, the basic information of the person-in-charge of the preparatory group, the personal approval certificate, the application form for the qualification of the proposed chairman and general manager, the identity certificate and a copy of the academic degree certificate;
(5) Draft articles of association of the insurance group company;
(six) the resolution of the shareholders’ (general) meeting of the insurance company to change its name and establish an insurance group company;
(7) The audited financial report and solvency report of the insurance company in the last three years;
(eight) the business license after the name change;
(9) documents certifying the ownership or right to use the domicile (business premises);
(ten) long-term development strategy and planning, business plan, foreign investment plan, capital and financial management, risk management and internal control and other major systems;
(eleven) information construction report;
(twelve) legal opinions;
(13) Anti-money laundering materials;
(14) A statement on the authenticity of the materials;
(fifteen) other materials stipulated by China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission.
Article 10 Where an insurance group company is established, the promoters or the insurance company to be renamed shall submit the following materials to China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission at the opening stage:
(1) An application for starting business, including the company’s name, domicile (business place), legal representative, registered capital, shareholding structure, business area and business scope, and the list of directors, supervisors, senior managers and key position managers to be proposed.
(2) If the establishment is initiated, the resolution of the founding meeting shall be provided; if there is no resolution of the founding meeting, the documents or resolutions of all investors agreeing to apply for business opening shall be submitted; In case of renaming, the resolution of the shareholders’ (general) meeting shall be provided.
(3) Articles of association of the insurance group company and rules of procedure of the shareholders’ (general) meeting, the board of directors and the board of supervisors.
(4) If the establishment is initiated, a capital verification report shall be provided; If the company adopts the method of renaming its establishment, it shall provide the asset appraisal report, customer and creditor rights protection plan and employee rights protection plan to be injected into the newly established insurance subsidiary.
(5) Development planning, including planning elements such as the company’s strategic objectives, business development, institutional development, solvency management, capital management, risk management and safeguard measures.
(6) Resumes of the directors, supervisors and senior managers to be appointed and the certification materials that meet the corresponding qualifications.
(7) The organizational structure of the company, including the establishment of departments and the basic composition of personnel.
(8) Asset custody agreement or letter of intent for asset custody cooperation.
(nine) the certificate of ownership or right to use the residence (business premises) and the fire safety certificate.
(ten) information construction report.
(eleven) the company’s internal management system.
(12) Business license.
(13) Relevant materials of investors, including financial information materials, tax payment certificates and credit records, information on the ownership structure, controlling shareholders and actual controllers, a statement of no record of major violations of laws and regulations, and a commitment letter for investment in self-owned funds.
(14) Anti-money laundering materials.
(15) A statement on the authenticity of the materials.
(sixteen) other materials stipulated by China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission.
Article 11 To establish an insurance group company, it shall register with the market supervision and management department in industrial and commercial registration and obtain a business license.
An insurance group company shall be approved by China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission before it can carry out relevant business activities. After approval by China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission, an insurance license shall be issued.
The time limit for examination and approval of the establishment of insurance group companies shall be implemented with reference to the relevant provisions of insurance companies.
Chapter III Operating Rules
Article 12 The business of an insurance group company is mainly equity investment and management.
Insurance group companies should use their own funds to carry out major equity investments. Major equity investment refers to the investment behavior of controlling the invested enterprise.
Article 13 An insurance group company shall abide by the requirements of laws, administrative regulations and other regulatory provisions in its insurance business, equity management and use of insurance funds.
Article 14 On the basis of respecting the operational autonomy of independent legal persons of subsidiaries and other member companies, insurance group companies shall make overall management of the equity investment of the whole group to prevent disorderly expansion.
Article 15 An insurance group company may invest in the following insurance enterprises:
(1) Insurance companies;
(2) Insurance asset management institutions;
(3) specialized insurance agencies, insurance brokerage agencies and insurance assessment agencies;
(four) other insurance enterprises approved by China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission.
Article 16 An insurance group company may invest in non-insurance financial enterprises.
The book balance of major equity investments made by insurance group companies and their subsidiaries in domestic non-insurance financial enterprises shall not exceed 30% of the consolidated net assets of the group at the end of last year.
Article 17 An insurance group company and its subsidiaries shall, in principle, not hold more than one share when investing in an enterprise with the same main business in the same financial industry.
Article 18 An insurance group company may invest in non-financial enterprises related to insurance business as stipulated in Article 56 of these Measures.
Except for non-financial enterprises and project companies established for investment in real estate as stipulated in Article 56 of these Measures, the shareholding ratio of an insurance group company to other single non-financial enterprises shall not exceed 25%, or it shall not have a significant impact on the enterprise.
Article 19 The total book balance of major equity investments made by insurance group companies and their financial subsidiaries in domestic non-financial enterprises shall not exceed 10% of the consolidated net assets of the group at the end of last year.
Non-financial enterprises included in the calculation scope of the preceding paragraph refer to the first-level non-financial enterprises invested by insurance group companies and their financial subsidiaries in China.
The non-financial enterprises mentioned in this Article do not include the project companies established by insurance group companies and their financial subsidiaries for investing in real estate, and the shared service subsidiaries mainly providing services for insurance groups as stipulated in Item (1) of Paragraph 1 of Article 56 of these Measures.
Article 20 An insurance group company may make overseas investments.
The book balance of major equity investments made by insurance group companies and their domestic subsidiaries in overseas entities shall not exceed 10% of the consolidated net assets of the group at the end of last year.
The overseas entities included in the calculation of the preceding paragraph refer to the first-level overseas entities invested by insurance group companies and their domestic subsidiaries abroad.
The book balance of an insurance group company and its domestic subsidiaries investing in a single overseas non-financial entity shall not exceed 5% of the consolidated net assets of the group at the end of the previous year.
The overseas entities specified in this article do not include the project companies established by insurance group companies and their domestic financial subsidiaries for investing in real estate.
Chapter IV Corporate Governance
Article 21 An insurance group company shall, in accordance with the requirements of laws, administrative regulations and other regulatory provisions, establish a corporate governance framework that meets the following requirements:
(1) Covering all member companies of the Group;
(2) Covering all important matters of the Group;
(3) properly identify and balance the conflicts of interest between the member companies and the group as a whole and among the member companies.
The contents that the governance framework should pay attention to include but not limited to:
(1) Standardized governance structure;
(two) the appropriateness of the ownership structure and management structure;
(3) Clear boundaries of responsibilities;
(4) Financial soundness of major shareholders;
(5) Scientific development strategy, values and good social responsibility;
(6) Effective risk management and internal control;
(7) Reasonable incentive and restraint mechanism;
(8) Perfect information disclosure system.
Article 22 An insurance group company shall respect the operational autonomy of its subsidiaries and other member companies as independent legal persons, make overall management of the group’s human resources, financial accounting, data governance, information system, capital utilization, brand culture and other matters, strengthen business collaboration and resource sharing within the group, establish a risk management, internal control compliance and internal audit system covering the whole group, and improve the overall operational efficiency and risk prevention capability of the group.
Article 23 An insurance group company shall not abuse its control position or take other improper measures to damage the legitimate rights and interests of its subsidiaries and other stakeholders in the process of performing its management functions.
Article 24 An insurance group company shall organize the formulation of the overall strategic plan of the group, regularly evaluate the implementation of the strategic plan, and adjust and improve the strategic plan according to the actual development and changes in the external environment.
An insurance group company shall, according to the overall strategic planning of the group, guide its subsidiaries to formulate development strategies and business plans. An insurance group company shall set up or designate corresponding functional departments to regularly monitor and evaluate the implementation of the development strategy and business plan of its subsidiaries and put forward management opinions to ensure the realization of the overall objectives of the group and the responsibility objectives of its subsidiaries.
Article 25 An insurance group company shall reasonably determine the size and membership of the board of directors according to its own management needs.
Article 26 The board of directors of an insurance group company shall set up a special committee according to relevant regulatory requirements and actual conditions, and exercise such functions as auditing, nomination and remuneration management, strategic management, risk management and related party transaction management.
Article 27 An insurance group company shall guide its subsidiaries to establish a standardized corporate governance structure according to the overall strategic planning of the group and the management needs of its subsidiaries and the principles of compliance, simplification and high efficiency.
If the subsidiary is a listed company, the corporate governance shall conform to the listing rules and the regulatory requirements of the listed company.
Article 28 An insurance group company shall, while promoting the good operation of its shareholders’ (general) meeting, board of directors and board of supervisors in accordance with the law, strengthen decision-making support and organizational management for different levels and types of meetings of its subsidiaries.
An insurance group company shall establish or designate corresponding functional departments to provide support and services for the directors and supervisors of its subsidiaries to perform their duties. Directors and supervisors of subsidiaries shall be responsible for their performance of duties in the board of directors or the board of supervisors according to law.
Article 29 An insurance group company may, after filing with China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission, exempt its insurance subsidiaries from the regulatory requirements on independent directors and special committees of the board of directors if it meets the following conditions:
(1) The insurance group has a sound corporate governance structure and an effective corporate governance mechanism, and has established a system of independent directors and special committees of the board of directors in accordance with relevant regulatory provisions;
(2) The insurance group company has established an effective control mechanism for its insurance subsidiaries.
In the event that an insurance subsidiary exempted in the preceding paragraph fails in its corporate governance mechanism or suffers from corporate governance defects, China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission may revoke the exemption as appropriate.
Article 30 An insurance group company shall have a concise, clear and penetrating equity structure.
An insurance group shall establish an organizational structure and management structure suitable for its strategic planning, risk status and management ability, so as to achieve a reasonable level of equity control of the insurance group company and its subordinate member companies, a clear and transparent organizational structure and a clear management structure.
Article 31 In principle, the level of equity control between an insurance group company and its financial subsidiaries shall not exceed three levels, and the level of equity control between its non-financial subsidiaries shall not exceed four levels. The calculation of the level of equity control is based on the level of the insurance group company. Special purpose entities that do not conduct business or actually operate, and project companies established to invest in real estate may not be counted in the above-mentioned equity control level.
Article 32 In principle, the member companies of an insurance group shall not cross-hold shares, and subsidiaries and other member companies shall not hold the shares of an insurance group company.
Article 33 In principle, the senior managers of an insurance group company may concurrently serve as the senior managers of at most one insurance subsidiary.
In principle, senior managers of subsidiaries and other member companies shall not concurrently hold positions with each other.
Article 34 An insurance group company shall establish and improve the performance evaluation system for directors, supervisors and senior managers covering the whole group.
An insurance group company shall establish a scientific and reasonable salary management mechanism and performance appraisal system that is compatible with the group’s development strategy, risk management, overall benefits, job responsibilities, social responsibilities and corporate culture.
Article 35 An insurance group company shall establish a unified internal audit system, conduct independent and objective supervision, evaluation and suggestions on the financial revenue and expenditure, business operation, internal control and risk management of the group and its member companies, and guide and evaluate the internal audit work of its subsidiaries.
If an insurance group company implements centralized or vertical management of internal audit, its subsidiaries may entrust the insurance group company to carry out internal audit.
Chapter V Risk Management
Article 36 An insurance group company shall integrate the group’s risk management resources, establish a comprehensive risk management system and a scientific and effective risk early warning mechanism that are suitable for the group’s strategic objectives, organizational structure and business model, and effectively identify, measure, evaluate, monitor and control the overall risks of the group.
Insurance group risks include but are not limited to:
(1) General risks, including insurance risk, credit risk, market risk, liquidity risk, operational risk, reputation risk and strategic risk;
(2) Unique risks, including risk contagion, opaque organizational structure, concentration risk, non-insurance risks, etc.
Article 37 An insurance group company shall set up a risk management department independent of the business department, responsible for the formulation and implementation of the group’s comprehensive risk management system, and require all business lines, subsidiaries and other member companies to formulate their own risk management policies under the framework of the group’s overall risk preference and risk management policies, so as to promote the consistency and effectiveness of the insurance group’s risk management.
Article 38 An insurance group company shall formulate a risk preference system at the group level, define the risk level that the group is willing and able to bear in the process of achieving its strategic objectives, determine the risk management objectives, and the risk tolerance and risk limit of the group for various risks.
The risk preference system shall be implemented after the approval of the board of directors, and shall be reviewed, revised and improved every year.
Article 39 An insurance group company shall, according to the overall development strategy and risk preference of the group, allocate various risk indicators and risk limits, and establish an over-limit disposal mechanism. The risk preference, risk tolerance and risk limit of subsidiaries and other member companies shall be coordinated with those of the Group.
An insurance group company shall monitor the implementation of the risk management system of the group as a whole, its subsidiaries and other member companies, and may require the member companies to adjust the risk limit based on the group risk limit when necessary.
Article 40 An insurance group company shall establish an information system to meet the needs of group risk management, ensure that it can obtain relevant information of group risk management accurately, comprehensively and timely, conduct qualitative and quantitative analysis of various risks, and effectively identify, evaluate and monitor the overall risk status of the group.
Article 41 An insurance group company shall manage the concentration risk of the group on the basis of consolidated statement, and establish and improve the policies, procedures and methods of concentration risk management, so as to identify, measure, monitor and prevent different types of concentration risks of the group as a whole and its member companies.
The concentration risk of insurance group refers to the risk that a single risk or risk combination of member companies may directly or indirectly threaten the solvency of the group after aggregation at the group level; Including but not limited to counterparty concentration risk, insurance business concentration risk, non-insurance business concentration risk, investment asset concentration risk, industry concentration risk, regional concentration risk, etc.
Article 42 An insurance group company shall establish and improve the firewall system in fund management, business operation, information management and personnel management within the group to prevent risk transmission among the member companies of the insurance group.
When conducting business collaboration among insurance group member companies, the risk-taking subjects shall be clearly defined in the form of contracts according to law, so as to prevent unclear risk responsibilities, cross-infection and conflicts of interest.
Article 43 An insurance group company shall establish policies and procedures for monitoring, reporting, controlling and handling related party transactions and internal transactions of the whole insurance group, so as to prevent possible improper interest transfer, delayed exposure of risks, regulatory arbitrage, risk contagion and other negative impacts on the stable operation of the insurance group.
The internal transactions of an insurance group shall comply with the relevant provisions of China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission on related party transactions and internal transactions.
Article 44 An insurance group company shall strengthen the overall management of the group’s external guarantee, and clarify the conditions, amount and approval procedures of the external guarantee.
An insurance group company can only provide guarantees to its insurance subsidiaries, and the balance of external guarantees provided by the insurance group company and its subsidiaries shall not exceed 10% of the company’s net assets at the end of the previous year.
Article 45 An insurance group company shall establish a stress test system suitable for its risks, conduct stress tests on the overall liquidity and solvency of the group on a regular basis, and apply the test results to the formulation of business management decisions, emergency plans and recovery and disposal plans.
Article 46 An insurance group company shall strengthen the information security protection of group customers, guide and urge its subsidiaries and other member companies to carry out the collection, transmission, storage, use and sharing of customer information in accordance with the principles of legality, justness and necessity, and strictly fulfill their information protection obligations.
Chapter VI Capital Management
Article 47 An insurance group company shall establish and improve a capital management system covering the whole group, including a capital planning mechanism, a capital adequacy evaluation mechanism, a capital restraint mechanism and a capital replenishment mechanism, so as to ensure that the capital is suitable for the asset scale, business complexity and risk characteristics, and can fully cover all kinds of risks faced by the group.
Article 48 An insurance group company shall, according to the company’s development strategic objectives, industry conditions and relevant state regulations, make targeted capital plans for the insurance group company and its financial subsidiaries for at least the next three years, and ensure the feasibility of the capital plans.
Article 49 An insurance group company shall set appropriate capital adequacy targets according to the group’s development strategy, business planning and risk preference.
Insurance group companies and their financial subsidiaries should establish a capital adequacy assessment mechanism that is suitable for their own risk characteristics and business environment, regularly assess their capital status, ensure that insurance group companies and their insurance subsidiaries meet the solvency supervision requirements, and the capital status of non-insurance financial subsidiaries continues to meet the requirements of financial supervision departments, and maintain the asset-liability ratio of non-financial subsidiaries at a reasonable level to achieve safe and stable operation of the group.
Article 50 An insurance group company shall establish a capital restraint mechanism within the group to guide its subsidiaries and other member companies to strictly abide by the capital restraint indicators, pay attention to prudent operation and strengthen risk management in formulating development strategies and business plans, designing products and using funds.
Insurance group companies shall strengthen the management of assets and liabilities, keep the debt scale and term structure reasonable and appropriate, and keep the asset structure and liability structure reasonably matched.
Article 51 An insurance group company shall establish a capital replenishment mechanism suitable for the development strategy and business planning of its subsidiaries and other member companies, maintain the group’s capital adequacy by strengthening business management, improving internal profitability, equity or debt financing, and strengthen cash flow management to fulfill its capital contribution obligations to its subsidiaries and other member companies.
Article 52 An insurance group company may issue qualified capital instruments according to laws, administrative regulations and other regulatory provisions, but the double leverage ratio shall be strictly controlled. The double leverage ratio of insurance group companies shall not be higher than the relevant requirements of China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission.
The term "double leverage ratio" as mentioned in these Measures refers to the ratio of the book value of the long-term equity investment of an insurance group company to the owner’s equity; Book value refers to the book balance minus impairment reserve.
Chapter VII Management of Non-insurance Subsidiaries
Article 53 The term "non-insurance subsidiaries" as mentioned in these Measures refers to the domestic and overseas subsidiaries directly or indirectly controlled by the insurance group company and its insurance subsidiaries, which do not belong to the insurance enterprises specified in Article 15 of these Measures.
Article 54 An insurance group company and its insurance subsidiaries directly or indirectly invest in non-insurance subsidiaries, which should be conducive to optimizing the group’s resource allocation, exerting synergy, enhancing the overall specialization level and market competitiveness of the group, and effectively promoting the development of the main insurance industry.
The term "direct investment" as mentioned in this chapter refers to the behavior of insurance group companies and their insurance subsidiaries to invest in the name of investors and hold the equity of non-insurance subsidiaries; The so-called indirect investment refers to the behavior of insurance group companies and their non-insurance subsidiaries at all levels to invest in the name of investors and hold the equity of other non-insurance subsidiaries.
Investing in non-insurance subsidiaries should follow the principle that substance is more important than form. In essence, the investment carried out by an insurance group company or its insurance subsidiaries shall not evade supervision by indirect investment through non-insurance subsidiaries in violation of regulations.
Article 55 An insurance group company shall establish a sound internal management system, define the authority, process and responsibility for the management of non-insurance subsidiaries, and implement the main responsibility for the management of non-insurance subsidiaries.
Article 56 An insurance group company may directly or indirectly invest in non-insurance subsidiaries, and the specific types include:
(1) A shared service subsidiary that mainly provides information technology services, auditing, policy management, catastrophe management, property management and other services and management for insurance group member companies;
(2) Other non-insurance subsidiaries established by carrying out major equity investment according to the regulatory provisions of China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission on the use of insurance funds;
(3) Other subsidiaries as stipulated by laws, administrative regulations and China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission.
Article 57 Where an insurance group company directly invests in a non-insurance subsidiary of shared services, it shall meet the following conditions:
(1) The corporate governance mechanism is sound and running well;
(2) At the end of the previous period, the comprehensive solvency adequacy ratio was above 150%, and the core solvency adequacy ratio was above 75%;
(three) the use of its own funds to invest, the source of funds in line with laws, administrative regulations and regulatory requirements;
(4) The non-insurance subsidiary with shared services to be invested mainly provides shared services for the insurance group;
(5) China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission’s regulatory provisions on major equity investments.
Insurance group companies may not indirectly invest in non-insurance subsidiaries of shared services.
Article 58 An insurance group company investing in a non-insurance subsidiary of shared services shall report to China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission for examination and approval, and provide the following materials:
(a) the materials that should be submitted for the major equity investment required by the relevant regulatory provisions of China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission;
(2) Specific plans for sharing services or management, institutional arrangements for risk isolation, and relevant measures for protecting the rights and interests of insurance consumers, etc.
The direct investment of insurance group companies in non-insurance subsidiaries other than shared services shall be implemented in accordance with the regulatory provisions of China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission on major equity investments.
Where an insurance group company indirectly invests in a non-insurance subsidiary, the insurance group company shall report to China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission within 15 working days from the date of signing the sponsor agreement or investment agreement.
Article 59 The direct investment of an insurance group company and its insurance subsidiaries in non-insurance subsidiaries shall conform to the internal decision-making procedures stipulated in laws, administrative regulations, regulatory provisions and its articles of association, and be approved by its shareholders’ (general meeting), board of directors or its authorized institutions.
Indirect investment in non-insurance subsidiaries shall be reported to the board of directors of the insurance group company or its insurance subsidiaries.
Article 60 An insurance group company and its insurance subsidiaries shall, through the management of the directly controlled non-insurance subsidiaries, ensure that other non-insurance subsidiaries invested or acquired by non-insurance subsidiaries comply with the relevant requirements of these Measures.
Article 61 An insurance group company shall strengthen the management of trademarks and shop names, and clarify the specific ways and authorities for non-insurance member companies to use their own trademarks and shop names, so as to avoid the transmission of reputation risks.
Article 62 An insurance group company and its insurance subsidiaries shall not provide guarantees for the debts of non-insurance subsidiaries, and shall not provide loans to non-insurance subsidiaries, unless otherwise stipulated by China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission.
Article 63 An insurance group company and its insurance subsidiaries may not invest in non-insurance subsidiaries by taking joint liability for the debts of the invested enterprise.
When an insurance group company and its insurance subsidiaries subscribe for shares of non-insurance subsidiaries or securities such as stocks and bonds issued by them, they shall abide by the regulatory provisions of China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission on the use of insurance funds.
Where an insurance group company and its insurance subsidiaries make commitments to increase investment or provide capital assistance to non-insurance subsidiaries in the future, they shall comply with relevant regulations and be approved by their shareholders’ meeting, the board of directors or their authorized institutions.
Article 64 An insurance group company and its insurance subsidiaries shall establish an outsourcing management system, specifying the scope, contents, forms, decision-making authority and procedures, follow-up management, rights, obligations and responsibilities of outsourcing parties, etc.
The term "outsourcing" as mentioned in these Measures refers to the behavior that an insurance group company and its insurance subsidiaries entrust some business activities or management functions that were originally handled by themselves to non-insurance subsidiaries or institutions outside the group for continuous processing.
Article 65 Where an insurance group company and its insurance subsidiaries outsource their business or functions, they shall conduct a risk assessment and be reviewed and approved by its board of directors or the agency authorized by the board of directors, so as to ensure that the entrusted party providing outsourcing services has good and stable financial status, high technical strength and service quality, complete management ability and strong ability to deal with emergencies.
When outsourcing, an insurance group company and its insurance subsidiaries shall sign a written contract with the trustee, specifying the outsourcing content, form, service price, customer information confidentiality requirements, rights and obligations of all parties, and liability for breach of contract. In the process of outsourcing, we should strengthen the risk monitoring of outsourcing activities, regularly review the performance of outsourcing business and functions in the annual risk assessment, conduct risk exposure analysis and other risk assessments, and report to the board of directors.
Insurance group companies and their insurance subsidiaries shall report to China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission 20 working days before the signing of the outsourcing contract. According to the risk status of the outsourcing behavior, China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission can take measures such as risk warning, meeting and talking, supervision and inquiry.
Article 66 An insurance group company shall submit the annual report of its non-insurance subsidiaries to China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission before April 30th every year. The report shall include the following contents:
(a) the overall situation of investment in non-insurance subsidiaries, including the number, level, business classification and operation, control, important internal control and risk management system of non-insurance subsidiaries;
(2) The equity structure diagram of non-insurance subsidiaries, including the hierarchy and calculation of non-insurance subsidiaries, and the equity proportion of insurance group companies and their insurance subsidiaries directly or indirectly investing in non-insurance subsidiaries, etc.;
(3) Basic information of the main senior managers of non-insurance subsidiaries;
(4) Risk assessment of non-insurance subsidiaries, including major related party transactions and major internal transactions, outsourcing management, firewall construction and asset-liability ratio of non-financial subsidiaries, etc.;
(5) The insurance group’s holding of changes in equity, a non-insurance subsidiary, and the reasons;
(six) other matters required by China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission.
The annual report of the non-insurance subsidiaries of the insurance group shall be submitted by the insurance group company.
Chapter VIII Information Disclosure
Article 67 An insurance group company shall, in accordance with the requirements of laws, administrative regulations and other regulatory provisions, follow the principles of completeness, accuracy, timeliness and effectiveness, and disclose information in a standardized manner.
Article 68 An insurance group company shall, in addition to disclosing its basic information according to the relevant regulatory provisions on information disclosure of insurance institutions, also disclose the basic information of the group as a whole, including:
(a) the ownership structure between the insurance group company and its subsidiaries at all levels;
(2) Basic information such as the name, registered capital, paid-in capital, shareholding structure and legal representative of the non-insurance subsidiary;
(3) Other matters stipulated by China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission.
Article 69 An insurance group company shall, in addition to disclosing its major events in accordance with the relevant regulatory provisions on information disclosure of insurance institutions, also disclose the following major events that have occurred in the group:
(1) Risk events that have a significant impact on the Group;
(two) other matters stipulated by China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission.
Article 70 An insurance group company shall prepare an annual information disclosure report, which shall at least include the following contents in addition to the company’s annual information disclosed in accordance with the relevant regulatory provisions on information disclosure of insurance institutions:
(1) Financial and accounting information under the consolidated caliber of the previous year;
(2) solvency information of the previous year;
(3) Major internal transactions between consolidated member companies of the insurance group in the previous year, except those that have been disclosed by member companies according to laws, administrative regulations and other regulatory requirements;
(4) The overall risk management status of the Group in the previous year;
(five) other matters stipulated by China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission.
Article 71 An insurance group company shall post the basic information, major events and annual information disclosure report of the company and the group as a whole on the company website.
If the basic situation changes, the insurance group company shall update it within 10 working days from the date of change.
In the event of a major event, the insurance group company shall issue a temporary information disclosure announcement within 15 working days from the date of the event.
The annual information disclosure report shall be released before April 30th of each year, unless otherwise stipulated by China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission.
The disclosure of information related to solvency shall be implemented in accordance with the relevant requirements of the solvency supervision rules of insurance companies.
Article 72 Relevant information that has been disclosed by a listed insurance group company in accordance with the information disclosure requirements of listed companies may not be disclosed repeatedly.
Chapter IX Supervision and Administration
Article 73 On the basis of supervision by a single legal person, China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission conducts comprehensive and continuous consolidated supervision on the capital, finance and risks of insurance groups, and identifies, measures, monitors and evaluates the overall risks of insurance groups.
Based on consolidated supervision, China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission can adopt direct or indirect supervision, and comprehensively monitor the risks of all member companies of insurance groups through insurance group companies or other regulated member companies according to law, and take corresponding measures when necessary.
The financial management department shall, in accordance with the division of responsibilities for financial supervision, supervise the insurance group companies and their financial member companies.
Article 74 China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission follows the principle that substance is more important than form, and determines the scope of consolidated supervision of insurance groups on the basis of control and taking into account the risk correlation.
Article 75 An insurance group company and its subsidiaries shall be included in the scope of consolidated supervision.
In addition to the circumstances specified in the preceding paragraph, the following institutions invested by insurance group companies shall be included in the scope of consolidated supervision:
(1) The risks or losses generated by the invested institution are sufficient to have a significant impact on the financial position and risk level of the insurance group;
(2) Other invested institutions established through complicated equity design such as domestic and overseas subsidiaries and shell companies, which are actually controlled by the insurance group or have a significant impact on the operation and management of the institution.
Article 76 China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission has the right to determine and adjust the scope of consolidated supervision and put forward supervision requirements according to the changes in the ownership structure, risk categories and risk status of insurance group companies.
The insurance group company shall report the consolidated scope and management to China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission.
Article 77 China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission may require the following units or individuals to provide materials and information related to the operation, management and financial status of an insurance group company within a specified time limit:
(1) A member company of an insurance group;
(2) Shareholders and actual controllers of the insurance group company;
(3) Directors, supervisors and senior managers of insurance group companies;
(four) other units or individuals that China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission considers it necessary to provide relevant information.
China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission can establish a tripartite meeting mechanism with insurance group companies and external auditors to learn about the insurance group’s corporate governance, risk prevention and control, and group management and control.
According to the Insurance Law and the relevant provisions of the financial supervision and coordination mechanism, China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission can ask the account opening banks, designated commercial banks, asset custody institutions, stock exchanges and securities registration and settlement institutions of the member companies of the insurance group to assist in the investigation.
Article 78 An insurance group company shall timely submit financial reports, solvency reports, consolidated supervision reports, reports of non-insurance subsidiaries and other relevant reports and other materials to China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission in accordance with relevant regulations.
Article 79 In case of major events that affect or may affect the operation and management, financial status, risk control and customer asset safety of an insurance group company, or major changes in the organizational structure, management structure or equity structure of an insurance group company, the insurance group company shall immediately submit a report to China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission, explaining the causes, current status, possible impacts and measures to be taken.
Article 80 If the capital adequacy level of the financial subsidiaries of an insurance group company fails to meet the requirements of the financial regulatory agency, China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission may require the insurance group company to ensure its capital adequacy by means of capital increase. If an insurance group company fails to implement the regulatory requirements, China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission can take corresponding measures according to law.
Article 81 If an insurance subsidiary of an insurance group company fails to meet the prudential supervision requirements stipulated by the financial regulatory agency, and its business or financial situation deteriorates significantly, China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission may require the insurance group company to take effective measures to help it resume its normal operation.
Article 82 If a non-insurance subsidiary significantly endangers the safe operation of an insurance group company or its insurance subsidiaries, China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission may require the insurance group company to make rectification.
Article 83 If the equity investment scope, proportion or equity control level of an insurance group company and its subsidiaries do not meet the regulatory requirements, China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission may take corresponding measures according to law.
Article 84 China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission may, based on the principle of prudential supervision, require insurance group companies to carry out stress tests covering the whole group on their solvency, liquidity and other risks, and take corresponding measures according to the results of the stress tests.
Article 85 China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission may require an insurance group company to make a recovery and disposal plan according to its asset scale, business complexity and risk status. The recovery plan should ensure the sustainability of the important business of the insurance group in the face of crisis; The disposal plan should avoid the negative impact on the industry caused by the interruption of the operation of the insurance group and minimize the consumption of public capital.
Article 86 China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission cooperates with other domestic regulatory agencies, shares regulatory information, coordinates regulatory policies and measures, and effectively supervises insurance group member companies to avoid regulatory vacuum and duplication.
China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission can carry out regulatory cooperation with overseas regulatory agencies by signing cross-border cooperation agreements or other forms, strengthen cross-border regulatory coordination and information sharing, and effectively supervise cross-border insurance groups.
Chapter X Supplementary Provisions
Article 87 The supervision and management of the merger, division, change, dissolution and business of insurance group companies, as well as the qualifications of relevant personnel, shall be implemented with reference to the relevant provisions of China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission on insurance companies.
Article 88 These Measures shall apply to foreign insurance companies or foreign insurance group companies that set up insurance group companies as shareholders of insurance companies in China. If there are special provisions in the Regulations on the Administration of Foreign-funded Insurance Companies and its detailed rules for implementation, those provisions shall prevail.
These Measures shall apply mutatis mutandis to insurance companies that have direct or indirect control over other insurance enterprises, but do not have the words "insurance group" or "insurance holding" in their names, and the first paragraph of Article 29 shall not apply.
Insurance groups recognized as systemically important financial institutions have special regulatory provisions, which shall prevail.
Article 89 The management of non-insurance subsidiaries directly or indirectly invested by insurance companies shall refer to the provisions of these Measures on non-insurance subsidiaries.
Except for branches of member companies of an insurance group, the unincorporated organizations of an insurance group shall be governed by the provisions of these Measures on member companies of an insurance group.
Article 90 The term "control" as mentioned in these Measures refers to the existence of one of the following circumstances:
(1) The investor directly or indirectly obtains more than half of the voting shares of the invested enterprise;
(2) The investor substantially owns more than half of the voting rights of the invested enterprise by signing agreements or other arrangements with other investors;
(3) According to the law or agreement, the investor has the power to actually control the behavior of the invested enterprise;
(4) The investor has the right to appoint or remove more than half of the members of the board of directors or other similar authority of the invested enterprise;
(five) the investor has more than half of the voting rights in the board of directors of the invested enterprise or other similar authority;
(6) Other circumstances under control, including those in accordance with the Accounting Standards for Enterprises No.33 — — The consolidated financial statements constitute a control situation.
When two or more investors are qualified to independently lead the decision-making, operation and management activities of the invested enterprise in different aspects, the party that can lead the activities that have the most significant impact on the return of the invested enterprise is regarded as forming control over the invested enterprise.
Article 91 The term "above", "at least" and "not less than" as mentioned in these Measures all include this number, and "exceeding" does not include this number.
Article 92 These Measures shall be interpreted by China Banking and Insurance Regulatory Commission.
Article 93 These Measures shall come into force as of the date of promulgation. The Measures for the Administration of Insurance Group Companies (Trial) issued by the former China Insurance Regulatory Commission (No.29 [2010] of China Insurance Regulatory Commission) shall be abolished at the same time. Where the provisions of the Guidelines for Consolidated Supervision of Insurance Groups (No.96 [2014] of China Insurance Regulatory Commission) are inconsistent with these Measures, these Measures shall prevail.